m (moved Dashboard to Community biology) |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
There are many successful communities within Red Hat, Fedora, and JBoss, and those communities have been built by many different people. The Community Architecture team wants to understand how these communities are created, and how we ensure that every member of Red Hat, Fedora, and JBoss is capable of creating and leading a successful community. | There are many successful communities within Red Hat, Fedora, and JBoss, and those communities have been built by many different people. The Community Architecture team wants to understand how these communities are created, and how we ensure that every member of Red Hat, Fedora, and JBoss is capable of creating and leading a successful community. | ||
== Community Biology 101 == | |||
Community serves as a catalyst in everything that Red Hat, Fedora, and JBoss does. | Community serves as a catalyst in everything that Red Hat, Fedora, and JBoss does. | ||
[[Image:Catalyst.png]] | [[Image:Catalyst.png]] | ||
http://www.columbia.edu/cu/biology/courses/c2005/purves6/figure06-14.jpg | <br> | ||
(http://www.columbia.edu/cu/biology/courses/c2005/purves6/figure06-14.jpg) | |||
'''Reaction:''' The progress of any task from ''idea'' to ''reality''. The task can be as simple as a one-page summary of Fedora 10 for the press, or as complicated as the feature planning process for Fedora 11. The task can be code, leadership, process documentation, testing, writing, artwork, etc. | '''Reaction:''' The progress of any task from ''idea'' to ''reality''. The task can be as simple as a one-page summary of Fedora 10 for the press, or as complicated as the feature planning process for Fedora 11. The task can be code, leadership, process documentation, testing, writing, artwork, etc. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 28: | ||
If we have done our job correctly, the '''activation energy''' needed to reach critical mass will be lower than in an equivalent reaction that did not focus on community building. | If we have done our job correctly, the '''activation energy''' needed to reach critical mass will be lower than in an equivalent reaction that did not focus on community building. | ||
[[Category:Community Architecture]] | [[Category:Community Architecture]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:09, 22 June 2010
There are many successful communities within Red Hat, Fedora, and JBoss, and those communities have been built by many different people. The Community Architecture team wants to understand how these communities are created, and how we ensure that every member of Red Hat, Fedora, and JBoss is capable of creating and leading a successful community.
Community Biology 101
Community serves as a catalyst in everything that Red Hat, Fedora, and JBoss does.
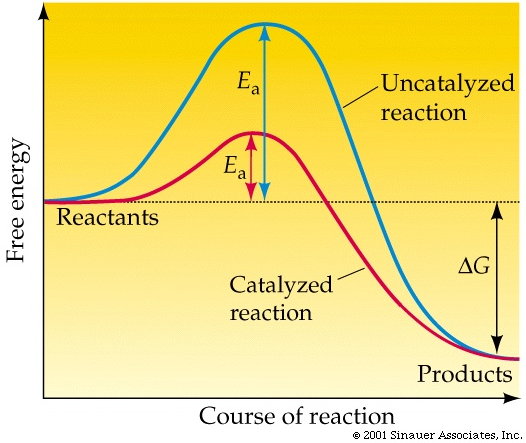
(http://www.columbia.edu/cu/biology/courses/c2005/purves6/figure06-14.jpg)
Reaction: The progress of any task from idea to reality. The task can be as simple as a one-page summary of Fedora 10 for the press, or as complicated as the feature planning process for Fedora 11. The task can be code, leadership, process documentation, testing, writing, artwork, etc.
For any reaction to complete requires some amount of energy. From a business point of view, energy, time, and money are all synonymous.
The blue curve represents a reaction that does not operate with a community-building mindset. Perhaps this is a proprietary software project, and community isn't even an option. Perhaps it is an open source upstream that is so focused on coding, it doesn't have the time to properly build a community. Either way, the amount of energy required to reach a successful end state is high.
The red curve represents a reaction that does operate with a strong community. Whether it is a Fedora sub-project, Fedora as a whole, the RPM upstream, OLPC, or an emerging technology like Cobbler or Func is irrelevant.
Note that both reactions ultimately reach the same end state. The difference is the energy required to get there. Microsoft and Red Hat can both produce an operating system. Our job is to ensure that Red Hat does so more efficiently, and community is the mechanism by which we achieve that.
Incremental vs. Continuous
We still need to define the end state of a successful community-catalyzed reaction. The end state has two characteristics:
- The community has a clearly identified critical path and roadmap for the future.
- The community has a clearly defined leadership structure that does not depend on any of the catalysts.
In short, the reaction will have reached critical mass. The Community Architecture team can disengage from day-to-day operations in the community, but the community will continue to grow and thrive. Perhaps certain members of the team still participate in the community because they choose to, but the community is self-sustaining. We have made ourselves redundant, and therefore free to choose a new community to catalyze.
If we have done our job correctly, the activation energy needed to reach critical mass will be lower than in an equivalent reaction that did not focus on community building.
