(→News) |
(→News) |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Zuul Based CI = | = Zuul Based CI = | ||
== Goals == | |||
* Bring CI infrastructure based on Zuul for projects hosted on pagure.io and src.fedoraproject.org. | |||
* Propose jobs and workflow of jobs around Pull Requests for Fedora packages (distgits on src.fedoraproject.org). | |||
== News == | == News == | ||
=== August 28, 2019 === | === November 13, 2019 === | ||
* Introduction of the service on the Fedora CI mailing list https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/ci@lists.fedoraproject.org/thread/CXDD2VYR6PHTR76JCJ5H5VEBIRG7YL37/ | |||
=== October 22, 2019 - Service is ready to be beta tested === | |||
* This wiki page contains the process to attach a repository from src.fedoraproject.org or pagure.io to Zuul. | |||
* Current known Issue: Sometime, src.fedoraproject.org, does not call Zuul event hooks (https://pagure.io/fedora-infrastructure/issue/8320). Then Zuul is unable to react and run jobs from Pagure events. This does not happen with pagure.io. This is a blocker for CI which needs to be reliable in order to gain confidence, I've pinged infra folks in that issue to help us debug it. | |||
=== August 28, 2019 - Created Taiga EPIC === | |||
* Created the Taiga EPIC with the stories to achieve in the goal to provide Pagure PR Zuul jobs for Fedora distgit: https://teams.fedoraproject.org/project/ci/epic/14 | * Created the Taiga EPIC with the stories to achieve in the goal to provide Pagure PR Zuul jobs for Fedora distgit: https://teams.fedoraproject.org/project/ci/epic/14 | ||
=== Flock 2019 === | === Flock 2019 === | ||
| Line 13: | Line 27: | ||
** video: not published yet | ** video: not published yet | ||
== What is Zuul == | == What is Zuul/Nodepool == | ||
Zuul [https://zuul-ci.org/] is the CI and gating system from the Open Infrastructure Project [https://www.openstack.org/news/view/426/kata-containers-and-zuul-are-first-pilot-projects-confirmed-as-toplevel-open-infrastructure-projects-by-the-openstack-foundation-board]. It is able to scale | Zuul [https://zuul-ci.org/] is the CI and gating system from the Open Infrastructure Project [https://www.openstack.org/news/view/426/kata-containers-and-zuul-are-first-pilot-projects-confirmed-as-toplevel-open-infrastructure-projects-by-the-openstack-foundation-board]. It is able to scale and handles by default features such as artifacts sharing between jobs and cross Git repositories testing. You can see Zuul in action here [https://zuul.opendev.org/t/openstack/status]. | ||
Below is a list of features proposed by Zuul and its companion Nodepool: | Below is a list of features proposed by Zuul and its companion Nodepool: | ||
| Line 24: | Line 38: | ||
* Speculative testing of new jobs before merging: jobs will be run as they are submitted to make sure they behave as expected. | * Speculative testing of new jobs before merging: jobs will be run as they are submitted to make sure they behave as expected. | ||
* Cross repositories dependencies: a jobs' workspace can include unmerged patches from other projects if specified | * Cross repositories dependencies: a jobs' workspace can include unmerged patches from other projects if specified | ||
* Cross provider: a jobs' workspace can include unmerged patches from other projects even when hosted on different provider like Github and Pagure. | |||
* Parallel job run, only capped by resources available or predefined quotas | * Parallel job run, only capped by resources available or predefined quotas | ||
* Automated jobs resources lifecycle management: resources like VMs or containers needed by a given job can be defined in-repository, spawned on demand at a job's start, and destroyed when the job is finished, or held for debugging | * Automated jobs resources lifecycle management: resources like VMs or containers needed by a given job can be defined in-repository, spawned on demand at a job's start, and destroyed when the job is finished, or held for debugging | ||
| Line 32: | Line 47: | ||
Until now, Zuul was only able to listen to Gerrit or Github events. Recently a new driver [https://review.opendev.org/604404/] allow Zuul to interface with Pagure as well. Pagure, Zuul and Nodepool could therefore combine into a very efficient CI/CD stack. | Until now, Zuul was only able to listen to Gerrit or Github events. Recently a new driver [https://review.opendev.org/604404/] allow Zuul to interface with Pagure as well. Pagure, Zuul and Nodepool could therefore combine into a very efficient CI/CD stack. | ||
== Pagure | == How to Zuul attach a Pagure repository on Zuul == | ||
=== Configure the repository for Zuul === | |||
In the project settings: | |||
* Add "zuul" as admin in settings/Users & Groups | |||
* In Project Options | |||
** Check "Notify on pull-request flag" | |||
** Web-hooks: | |||
*** For a repository hosted on pagure.io add: https://softwarefactory-project.io/zuul/api/connection/pagure.io/payload | |||
*** For a repository hosted on src.fedoraproject.org add: https://softwarefactory-project.io/zuul/api/connection/src.fedoraproject.org/payload | |||
** (For gating, optional) | |||
*** Minimum score to merge pull-request: 0 | |||
*** Tags: Add the "gateit" tag | |||
This helper script could be used to ease the setup: | |||
https://pagure.io/fedora-project-config/blob/master/f/tools/project-settings-helper | |||
=== Add the repository into the Zuul configuration === | |||
Open a Pull Request on https://pagure.io/fedora-project-config | |||
Edit resources/fedora.yaml and add the repository such as: | |||
* For a repository hosted on pagure.io: | |||
resources: | |||
projects: | |||
Fedora-Zuul-CI: | |||
... | |||
source-repositories: | |||
... | |||
- '''repository-name''' | |||
* | * For a repository hosted on src.fedoraproject.org: | ||
resources: | |||
projects: | |||
Fedora-Zuul-CI: | |||
... | |||
source-repositories: | |||
... | |||
- '''repository-name''': | |||
'''connection: src.fedoraproject.org''' | |||
'''zuul/include: []''' | |||
Once the Pull Request is accepted and merged, the repository should be available in the Zuul project list: https://fedora.softwarefactory-project.io/zuul/projects | |||
=== Attach packaging jobs for a distgit repository on src.fedoraproject.org === | |||
We have managed to provide some standard Pull Request's jobs and workflow. This idea is to reduce the amount of manual steps to propose packaging changes to Fedora by taking advantage of CI. | |||
We propose a set of templates (a template can be seen as a workfow of jobs reacting to Pull Request events). Templates are available here https://pagure.io/fedora-zuul-jobs/blob/master/f/zuul.d/templates.yaml. | |||
Templates configure jobs through three types of pipeline (not the same as Jenkins/Gitlab pipeline concept): | |||
* '''check''': Jobs within that pipeline are triggered when a Pull Request is Opened or Updated | |||
* '''gate''': Jobs within that pipeline are triggered when a Pull Request is approved (prior to be merged and closed) | |||
* '''promote''': Jobs with that pipeline are triggered when a Pull Request is closed and merged | |||
Available jobs are: | |||
* '''rpm-scratch-build''': Runs a scratch build on Koji (Koji target based on the PR's branch) and retrieves artifacts on the test node (rpms). | |||
* '''rpm-build''': Runs a regular build on Koji (Koji target based on the PR's branch) | |||
* '''rpm-lint''': Runs a rpmlint on artifacts (rpms) passed from the parent job | |||
* '''rpm-rpminspect''': Runs rpminspect on artifacts (rpms) passed from the parent job. The job also finds the latest build on the related Koji tag and passes it to the rpminspect job so you get the rpminspect diff. | |||
* '''rpm-test''': Executes distgit embedded tests ''tests/tests.yml'' on the related Fedora node (rawhide VM for master branch, Fedora 30 VM for f30 branch, ...). It is compatible with the '''Fedora standard-test-interface''' as STI dependencies are available on the node. | |||
Available templates are: | |||
* '''build''': runs the ''rpm-scratch-build'' job in the check pipeline. | |||
* '''build-lint''': runs the ''rpm-scratch-build'' job then runs the ''rpm-linter'' + ''rpm-rpminspect'' jobs against the rpms built by the parent job. | |||
* '''build-lint-test''': runs the ''rpm-scratch-build'' job then runs the ''rpm-linter'' + ''rpm-rpminspect'' + ''rpm-test'' jobs against the rpms built by the parent job. | |||
* '''build-lint-test-gate''': same as '''build-lint-test''' + the CI will merge the Pull Request if the Pull Request receive the metadata tag "gateit" (from the Pagure UI) and the PR CI status is ''passed''. | |||
* '''build-lint-test-gate-promote''': same as '''build-lint-test-gate''' + rpm-build (regular koji build) when the Pull Request is merged and closed. | |||
There are some other templates available that I won't describe here but now you should have a better understanding about the concept so simply look at https://pagure.io/fedora-zuul-jobs/blob/master/f/zuul.d/templates.yaml. | |||
To attach a template to a repository you need to open a Pull Request on https://pagure.io/fedora-zuul-jobs-config. | |||
Edit zuul.d/projects.yaml to add: | |||
- project: | |||
name: '''repository''' | |||
templates: | |||
- '''build-lint-gate-promote''' | |||
repository should be like "rpms/python-gear". | |||
Once the Pull Request is merged, the jobs of the chosen template can be displayed by clicking on the related project on the page https://fedora.softwarefactory-project.io/zuul/projects. | |||
Currently f29, f30, f31 and master branches are supported. Only the x86_64 arch is supported. | |||
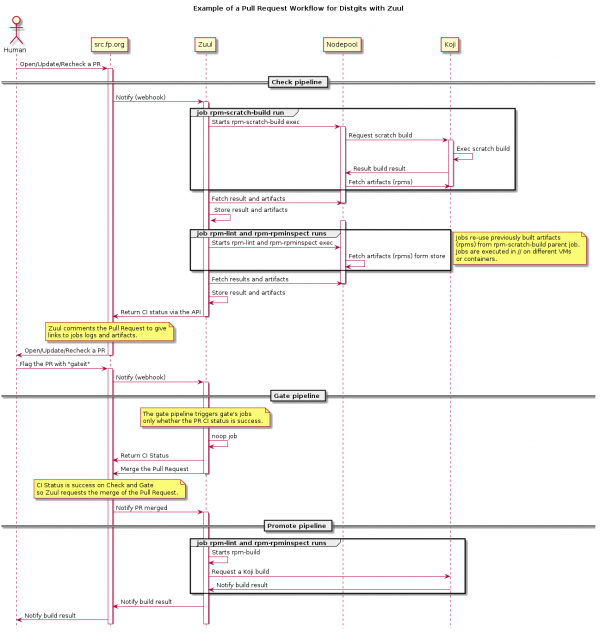
=== | === Sequence diagram of the PR workflow === | ||
This diagram shows interactions between components involved in this workflow and how they interact. The '''build-lint-gate-promote''' template is used in the example. | |||
[[File:Distgit-pr-workflow.png|600px]] | |||
=== Example of PR managed with that workflow === | |||
* | * https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/nodepool/pull-request/6 | ||
== Nodepool nodes == | |||
Jobs are configured to execute on a Fedora VM. The default jobs we provide are configured to use the right node based on the PR target branch. For instance the rpm-test job for the master branch execute on a rawhide VM. | |||
* Fedora rawhide cloud image (VM) https://softwarefactory-project.io/cgit/config/tree/nodepool/elements/virt-customize/fedora-rawhide-cloud.yaml | |||
* Fedora 31 cloud image (VM) https://softwarefactory-project.io/cgit/config/tree/nodepool/elements/virt-customize/fedora-31-cloud.yaml | |||
* Fedora 30 cloud image (VM) https://softwarefactory-project.io/cgit/config/tree/nodepool/elements/virt-customize/fedora-30-cloud.yaml | |||
* Fedora 29 cloud image (VM) https://softwarefactory-project.io/cgit/config/tree/nodepool/elements/virt-customize/fedora-29-cloud.yaml | |||
== Projects using Zuul for the PR workflow == | |||
* https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/nodepool | |||
* https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/python-gear | |||
* https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/python-zuul-sphinx | |||
== FAQ == | |||
=== | === How to attach automatically several repositories with Zuul === | ||
I would suggest to start with few packages first. | |||
For more packages this need to be automated. We don't have yet the tooling to onboard projects | |||
automatically but at a first glance, the Pagure API provides endpoints to update project ACLs and options | |||
so it should be possible to update automatically project settings. However for the PR | |||
approval part it seems the endpoint to manage allowed PR metadata tags is missing. | |||
The rest is simply YAML files to edit and two PRs to open. This can be done automatically as well. | |||
=== Why does zuul need to be an admin on the repository ? === | |||
That's a good question. Ideally the commit access would have only be needed (Zuul is | |||
also a gating system, it merges the code) but dealing with the events and API | |||
brings some difficulties at authentication level. Here is the explanation. | |||
Zuul needs to receive Pull Request and Git repo events but also it needs to be | |||
able to act on the PR via the API. To receive events Zuul relies on the Pagure Web Hook | |||
feature, Zuul serves an HTTP endpoint that Pagure uses to send payloads in case of | |||
events. Payloads need to be authenticated, to do so Zuul needs to know the | |||
Web Hook token configured in Pagure in the repository settings. To use the API Zuul | |||
needs the repository API key. Both the Web Hook Token and the API Key are | |||
unique per repository on Pagure. For each configured Pagure repository, Zuul will | |||
discover the Web Hook Token and create/reuse an API key via the Pagure API | |||
(connector endpoint) and this requires admin right on the related repository. | |||
I'm not aware of other ready to use solutions for that use case. For instance, to mitigate | |||
this, in the future Pagure could provide another user role level with commit access + | |||
access to the connector endpoint. In fact having this would ease third party application | |||
integration with Pagure. For instance on Github, there is that concept of application and | |||
Zuul relies on it to integrate easily with Github repositories. | |||
== Contacts == | |||
For any questions or issues you can contact ''fbo'' on freenode on #fedora-ci or #softwarefactory or you can create an issue on https://pagure.io/fedora-zuul-jobs/issues. | |||
Also the work in progress and next steps are tracked into that Taiga EPIC: https://teams.fedoraproject.org/project/ci/epic/14 | |||
Revision as of 16:40, 22 November 2019
Zuul Based CI
Goals
- Bring CI infrastructure based on Zuul for projects hosted on pagure.io and src.fedoraproject.org.
- Propose jobs and workflow of jobs around Pull Requests for Fedora packages (distgits on src.fedoraproject.org).
News
November 13, 2019
- Introduction of the service on the Fedora CI mailing list https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/ci@lists.fedoraproject.org/thread/CXDD2VYR6PHTR76JCJ5H5VEBIRG7YL37/
October 22, 2019 - Service is ready to be beta tested
- This wiki page contains the process to attach a repository from src.fedoraproject.org or pagure.io to Zuul.
- Current known Issue: Sometime, src.fedoraproject.org, does not call Zuul event hooks (https://pagure.io/fedora-infrastructure/issue/8320). Then Zuul is unable to react and run jobs from Pagure events. This does not happen with pagure.io. This is a blocker for CI which needs to be reliable in order to gain confidence, I've pinged infra folks in that issue to help us debug it.
August 28, 2019 - Created Taiga EPIC
- Created the Taiga EPIC with the stories to achieve in the goal to provide Pagure PR Zuul jobs for Fedora distgit: https://teams.fedoraproject.org/project/ci/epic/14
Flock 2019
- Talk: Pagure CI based on Zuul:
- slides: File:Slides-flock2019.pdf
- video: not published yet
What is Zuul/Nodepool
Zuul [1] is the CI and gating system from the Open Infrastructure Project [2]. It is able to scale and handles by default features such as artifacts sharing between jobs and cross Git repositories testing. You can see Zuul in action here [3].
Below is a list of features proposed by Zuul and its companion Nodepool:
- Event-driven pipelines based on Code-Review or Pull-Request workflow: jobs can be triggered automatically when a PR is submitted, changed, approved, merged, or when the repository is tagged.
- CI-as-code: jobs are defined as YAML + Ansible playbooks, pipeline definitions as YAML files. Zuul reads and loads those definitions directly from Git repositories.
- Support for jobs inheritance, jobs dependencies, jobs chaining (with artifacts sharing).
- Speculative testing of new jobs before merging: jobs will be run as they are submitted to make sure they behave as expected.
- Cross repositories dependencies: a jobs' workspace can include unmerged patches from other projects if specified
- Cross provider: a jobs' workspace can include unmerged patches from other projects even when hosted on different provider like Github and Pagure.
- Parallel job run, only capped by resources available or predefined quotas
- Automated jobs resources lifecycle management: resources like VMs or containers needed by a given job can be defined in-repository, spawned on demand at a job's start, and destroyed when the job is finished, or held for debugging
- Job resources support of OpenStack, OpenShift, K8S, Static nodes, AWS.
- Well-defined, reproducible job environments to eliminate flakiness
- Speculative testing before merging (gating): if several patches are about to land at the same time, they are tested on the repository's future state.
Until now, Zuul was only able to listen to Gerrit or Github events. Recently a new driver [4] allow Zuul to interface with Pagure as well. Pagure, Zuul and Nodepool could therefore combine into a very efficient CI/CD stack.
How to Zuul attach a Pagure repository on Zuul
Configure the repository for Zuul
In the project settings:
- Add "zuul" as admin in settings/Users & Groups
- In Project Options
- Check "Notify on pull-request flag"
- Web-hooks:
- For a repository hosted on pagure.io add: https://softwarefactory-project.io/zuul/api/connection/pagure.io/payload
- For a repository hosted on src.fedoraproject.org add: https://softwarefactory-project.io/zuul/api/connection/src.fedoraproject.org/payload
- (For gating, optional)
- Minimum score to merge pull-request: 0
- Tags: Add the "gateit" tag
This helper script could be used to ease the setup: https://pagure.io/fedora-project-config/blob/master/f/tools/project-settings-helper
Add the repository into the Zuul configuration
Open a Pull Request on https://pagure.io/fedora-project-config
Edit resources/fedora.yaml and add the repository such as:
- For a repository hosted on pagure.io:
resources:
projects:
Fedora-Zuul-CI:
...
source-repositories:
...
- repository-name
- For a repository hosted on src.fedoraproject.org:
resources:
projects:
Fedora-Zuul-CI:
...
source-repositories:
...
- repository-name:
connection: src.fedoraproject.org
zuul/include: []
Once the Pull Request is accepted and merged, the repository should be available in the Zuul project list: https://fedora.softwarefactory-project.io/zuul/projects
Attach packaging jobs for a distgit repository on src.fedoraproject.org
We have managed to provide some standard Pull Request's jobs and workflow. This idea is to reduce the amount of manual steps to propose packaging changes to Fedora by taking advantage of CI.
We propose a set of templates (a template can be seen as a workfow of jobs reacting to Pull Request events). Templates are available here https://pagure.io/fedora-zuul-jobs/blob/master/f/zuul.d/templates.yaml.
Templates configure jobs through three types of pipeline (not the same as Jenkins/Gitlab pipeline concept):
- check: Jobs within that pipeline are triggered when a Pull Request is Opened or Updated
- gate: Jobs within that pipeline are triggered when a Pull Request is approved (prior to be merged and closed)
- promote: Jobs with that pipeline are triggered when a Pull Request is closed and merged
Available jobs are:
- rpm-scratch-build: Runs a scratch build on Koji (Koji target based on the PR's branch) and retrieves artifacts on the test node (rpms).
- rpm-build: Runs a regular build on Koji (Koji target based on the PR's branch)
- rpm-lint: Runs a rpmlint on artifacts (rpms) passed from the parent job
- rpm-rpminspect: Runs rpminspect on artifacts (rpms) passed from the parent job. The job also finds the latest build on the related Koji tag and passes it to the rpminspect job so you get the rpminspect diff.
- rpm-test: Executes distgit embedded tests tests/tests.yml on the related Fedora node (rawhide VM for master branch, Fedora 30 VM for f30 branch, ...). It is compatible with the Fedora standard-test-interface as STI dependencies are available on the node.
Available templates are:
- build: runs the rpm-scratch-build job in the check pipeline.
- build-lint: runs the rpm-scratch-build job then runs the rpm-linter + rpm-rpminspect jobs against the rpms built by the parent job.
- build-lint-test: runs the rpm-scratch-build job then runs the rpm-linter + rpm-rpminspect + rpm-test jobs against the rpms built by the parent job.
- build-lint-test-gate: same as build-lint-test + the CI will merge the Pull Request if the Pull Request receive the metadata tag "gateit" (from the Pagure UI) and the PR CI status is passed.
- build-lint-test-gate-promote: same as build-lint-test-gate + rpm-build (regular koji build) when the Pull Request is merged and closed.
There are some other templates available that I won't describe here but now you should have a better understanding about the concept so simply look at https://pagure.io/fedora-zuul-jobs/blob/master/f/zuul.d/templates.yaml.
To attach a template to a repository you need to open a Pull Request on https://pagure.io/fedora-zuul-jobs-config.
Edit zuul.d/projects.yaml to add:
- project:
name: repository
templates:
- build-lint-gate-promote
repository should be like "rpms/python-gear".
Once the Pull Request is merged, the jobs of the chosen template can be displayed by clicking on the related project on the page https://fedora.softwarefactory-project.io/zuul/projects.
Currently f29, f30, f31 and master branches are supported. Only the x86_64 arch is supported.
Sequence diagram of the PR workflow
This diagram shows interactions between components involved in this workflow and how they interact. The build-lint-gate-promote template is used in the example.
Example of PR managed with that workflow
Nodepool nodes
Jobs are configured to execute on a Fedora VM. The default jobs we provide are configured to use the right node based on the PR target branch. For instance the rpm-test job for the master branch execute on a rawhide VM.
- Fedora rawhide cloud image (VM) https://softwarefactory-project.io/cgit/config/tree/nodepool/elements/virt-customize/fedora-rawhide-cloud.yaml
- Fedora 31 cloud image (VM) https://softwarefactory-project.io/cgit/config/tree/nodepool/elements/virt-customize/fedora-31-cloud.yaml
- Fedora 30 cloud image (VM) https://softwarefactory-project.io/cgit/config/tree/nodepool/elements/virt-customize/fedora-30-cloud.yaml
- Fedora 29 cloud image (VM) https://softwarefactory-project.io/cgit/config/tree/nodepool/elements/virt-customize/fedora-29-cloud.yaml
Projects using Zuul for the PR workflow
- https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/nodepool
- https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/python-gear
- https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/python-zuul-sphinx
FAQ
How to attach automatically several repositories with Zuul
I would suggest to start with few packages first.
For more packages this need to be automated. We don't have yet the tooling to onboard projects automatically but at a first glance, the Pagure API provides endpoints to update project ACLs and options so it should be possible to update automatically project settings. However for the PR approval part it seems the endpoint to manage allowed PR metadata tags is missing.
The rest is simply YAML files to edit and two PRs to open. This can be done automatically as well.
Why does zuul need to be an admin on the repository ?
That's a good question. Ideally the commit access would have only be needed (Zuul is also a gating system, it merges the code) but dealing with the events and API brings some difficulties at authentication level. Here is the explanation. Zuul needs to receive Pull Request and Git repo events but also it needs to be able to act on the PR via the API. To receive events Zuul relies on the Pagure Web Hook feature, Zuul serves an HTTP endpoint that Pagure uses to send payloads in case of events. Payloads need to be authenticated, to do so Zuul needs to know the Web Hook token configured in Pagure in the repository settings. To use the API Zuul needs the repository API key. Both the Web Hook Token and the API Key are unique per repository on Pagure. For each configured Pagure repository, Zuul will discover the Web Hook Token and create/reuse an API key via the Pagure API (connector endpoint) and this requires admin right on the related repository.
I'm not aware of other ready to use solutions for that use case. For instance, to mitigate this, in the future Pagure could provide another user role level with commit access + access to the connector endpoint. In fact having this would ease third party application integration with Pagure. For instance on Github, there is that concept of application and Zuul relies on it to integrate easily with Github repositories.
Contacts
For any questions or issues you can contact fbo on freenode on #fedora-ci or #softwarefactory or you can create an issue on https://pagure.io/fedora-zuul-jobs/issues.
Also the work in progress and next steps are tracked into that Taiga EPIC: https://teams.fedoraproject.org/project/ci/epic/14